Blog Details
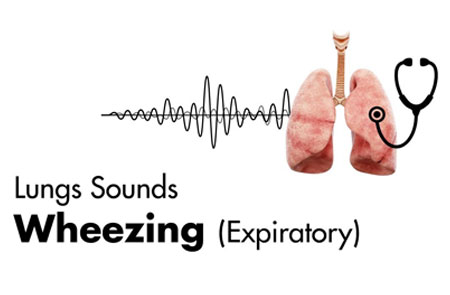
Asthma is a chronic condition that affects a large number of populations worldwide. As per WHO, in 2019, asthma affected 262 million people and caused 455,000 deaths. Asthma causes difficulty in breathing, coughing and wheezing. Wheezing is one of the typical symptoms of asthma. Asthma wheezing refers to a high-pitched, whistling sound while exhaling the air out. During asthma, airway becomes narrow and hence air passing though narrow airway produces wheezing sound.
Asthma wheezing is more common during exhalation and indicates mild or partial airway obstruction. In severe asthma, no wheeze may be heard as the airflow will be severely narrowed, and chest auscultation will be silent. In rare cases it may occur during inhalation as well. When asthma wheezing is present during inhalation as well as exhalation, it indicates a more serious condition and requires immediate medical treatment. In most cases, asthma patient can hear/feel their wheezing breathing sounds. But in some cases, it is identified by a physician only during the physical examination with the aid of a stethoscope.
Although asthma is one of the most common causes, wheezing can be caused by other disease conditions like congestive heart failure, foreign body obstruction or tumor in the airways. The presence of wheezing does not always mean that the patient has asthma, and a proper history and physical exam are required to make the diagnosis.
What are the causes, types and sounds of asthma wheezing? And what is the treatment option for asthma wheezing? Read on to know more!
Asthma is an allergic respiratory condition that causes inflammation and swelling in the airways. Asthma patients have a higher sensitivity towards allergens like mold, dust, animal dander and other irritants. Moreover, other viral illnesses like severe cough and cold also increase the chances of airway inflammation.
When a sensitive person comes in contact with these allergens or has exposure to certain triggers like cold air, dust etc., it causes an inflammation in the airways which results in increased mucus secretion and narrowed airways. These pathological changes lead to less passage for air during respiration and causes asthma wheezing.
Here are some common triggers that cause asthma wheezing:
There are mainly two types of asthma wheezing.
Expiratory asthma wheezing: As the name suggests, expiratory asthma wheezing occurs during exhalation. Expiratory asthma wheezing is more commonly seen in asthma patients. It is caused by mild airway obstruction. Some expiratory wheezing does not require specific treatment and gets cured on its own within a few days.
Inspiratory asthma wheezing: Inspiratory asthma wheezing occurs during inspiration. They are less common than expiratory asthma wheezing. When a patient has inspiratory wheezing or stridor over the neck, it indicates the presence of upper airway obstruction and requires immediate medical attention.
Asthma wheezing sounds are different in different people. It depends on the level of airway obstruction. Some patients define it as hoarse or squeaky noise, while for some it is more musical and sharper. Clinical studies have shown that the duration and pitch of the wheeze are co-related to the severity of airway obstruction.
Generally, the upper airway obstruction causes hoarse asthma wheezing, while a lower airway obstruction causes a musical type (similar to a wind music instrument) of asthma wheezing. Asthma wheezing can be caused by localized or generalized airway obstruction. When there is severe airway obstruction, it causes very little or no airflow which indicates a more serious condition and results in no wheezing sound.
Diagnosis of asthma wheezing is based on the presence of sign-symptoms, general physical examination and lab testing. Your doctor will ask different questions regarding your wheezing symptoms. such as: at what time of the day your wheezing symptoms get worse. Or do you have any allergy to a specific food? And do you smoke or have a family history of asthma? Clinical examination also includes examining lung sounds and checking the oxygen saturation level.
Apart from that, your doctor may also perform an X-ray, pulmonary function test and blood test to confirm the disease diagnosis.
The treatment option for asthma wheezing depends upon various factors like age and severity of symptoms. Your physician can decide the best treatment option for you as per your specific disease symptoms.
In general, asthma wheezing treatment has two options:
Short-term asthma medications: short-term asthma medication aims at relieving asthma wheezing and other acute symptoms of an asthma attack. Short-term asthma medications like bronchodilators dilate the narrowed airways and help prevent asthma flare-ups. Short-acting beta-agonists (SABA), and anticholinergics are some of the most commonly used short-acting asthma medications. These medications are only to be used on need basis and are not recommended to be used regularly for managing your asthma.
Long-term asthma control medications: Long-term asthma medication focuses on preventing relapses and reducing the swelling and obstruction in the airways. You have to take your long-acting asthma medication regularly, even when you have no active asthma symptoms. Corticosteroids, inhaled long-acting bronchodilators are the most commonly used long-acting asthma medications. These medications are recommended to be taken regularly to manage your asthma.
Leukotriene modifiers and mast cell stabilizers are some of the other asthma medications that help in reducing asthma wheezing and preventing asthma attacks.
Asthma wheezing could be mild or could be severe and life-threatening. Here are some warning signs of asthma wheezing that require immediate medical treatment:
Asthma is a chronic disease condition that cannot be cured. Living with a lung condition like asthma is challenging, but you can manage your asthma symptoms successfully with the help of asthma medication and other lifestyle changes.
Here are some crucial steps that help in managing your asthma symptoms and preventing asthma flare-ups.
Regular medical check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are important for preventing asthma flare-ups. Your doctor can prescribe and change the medications as per your existing symptoms.
Take your medication including inhalers and oral medications regularly
Next, it is important to take your medication including inhalers and oral medication as per your doctor’s prescription regularly. Asthma symptoms get better when you start taking asthma medication. However, it does not mean that you can stop your prescribed medication once your symptoms are resolved. You should not make any changes in your medication without concerning your doctor.
Follow a healthy lifestyle
As the next important step, it is important to follow a healthy lifestyle that includes eating a healthy diet and performing regular physical exercise. Eating a healthy diet (including more fruits, vegetables and whole grains) and exercising keep your immune system stronger and helps in preventing asthma flare-ups. If your asthma symptoms get worse by exercise, then you can discuss safe exercise options and short-acting asthma medication with your doctor, which can help in preventing asthma attacks while exercising.
Manage your stress level
Higher stress level is one of the main culprits of asthma flare-ups in many asthma patients. It is important to manage your stress levels. You can try meditation, progressive muscular relaxation or other stress-relieving techniques to manage your stress level, which helps a lot in preventing asthma flare-ups.
© 2026 Healthy Lungs.